In January 2026, the cryptocurrency market experienced a significant downturn, driven primarily by macroeconomic uncertainties and inflated valuations across both traditional and digital assets. The absence of substantial positive developments further exacerbated the situation, leading to a challenging environment for investors.
During the Federal Reserve”s meeting on January 27–28, a clear message was communicated: interest rates would remain steady between 3.5% and 3.75%. This decision reflected the Fed”s commitment to maintaining a restrictive monetary policy as inflation persisted above target levels. The immediate aftermath saw Bitcoin plummet from $90,400 to $83,383, marking a sharp decline of 7.3% within just 48 hours. This event underscored the cryptocurrency”s heightened sensitivity to monetary policies.
The appointment of Kevin Warsh as the next Federal Reserve Chair, effective May 15, 2026, sparked some optimism regarding potential policy adjustments in the future. However, investor sentiment remained skeptical about the likelihood of significant easing in the near term.
Trade policy also played a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. The imposition of high tariffs by the Trump administration added layers of uncertainty, with the average applied tariff rate reaching 14.0%—the highest since 1946. This aggressive tariff strategy is projected to negatively impact GDP growth and increase unemployment.
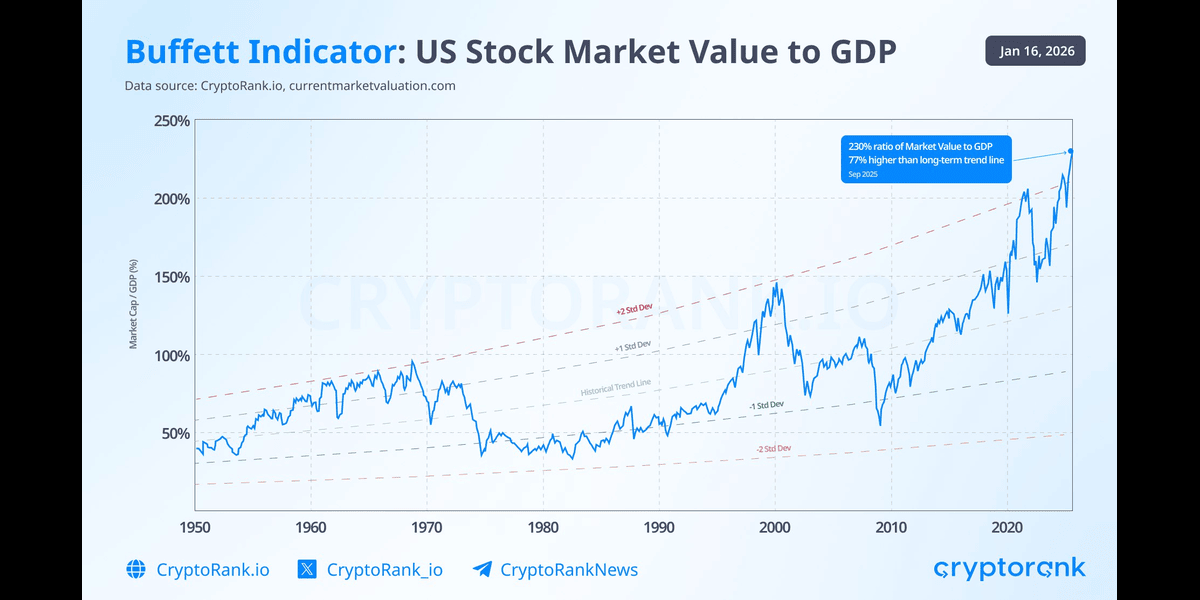
Valuation concerns in the traditional equity markets further compounded the pressure on cryptocurrencies. The Buffett Indicator indicated that the total stock market capitalization relative to GDP had soared to approximately 205%, significantly exceeding historical averages. Such metrics traditionally signal overvaluation, suggesting that a correction could be imminent, which would likely impact Bitcoin and the broader crypto market due to their increasing correlation with U.S. equities.
As Bitcoin closed January down 10%, it marked a fourth consecutive month of losses, highlighting its struggle amid bearish sentiments. In stark contrast, metals gained momentum, with silver emerging as a key asset in the market.
Ethereum also faced challenges, dropping 17.7% in January, its fifth straight month of decline. Despite significant technical enhancements aimed at improving user experience, these upgrades failed to translate into price recovery, raising concerns that the market had already factored in these improvements.
On the other hand, the activity surrounding prediction markets and real-world asset (RWA) tokenization showcased resilience during this downturn. The prediction market sector saw its spot volume rise by 50% month-over-month, achieving a new all-time high of $27 billion. Similarly, the RWA market witnessed a surge in value, reaching an all-time high of $23.7 billion, with tokenized U.S. Treasuries leading this growth.
The landscape of leading blockchains also displayed varied performance. Solana experienced a revival in memecoin activity, while TRON set records for active addresses and on-chain transactions. Meanwhile, BNB Chain achieved an all-time high in monthly active addresses despite a decline in overall trading volume.
In summary, the crypto market”s intertwining with the broader economic landscape suggests that its future trajectory will be heavily influenced by macroeconomic performance, regulatory changes, and shifts in global asset demand. While sectors like prediction markets and RWA tokenization demonstrate growth potential, the overall market remains under pressure as it navigates significant challenges.