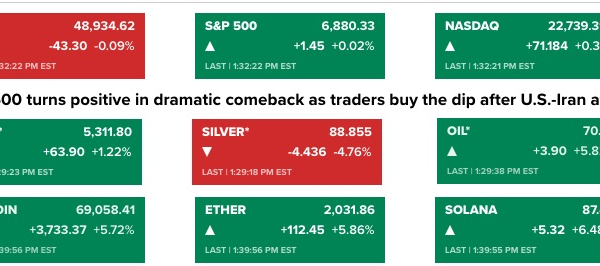
Crypto synthetic assets represent a transformative approach to financial markets, allowing for enhanced accessibility to traditional assets like stocks, gold, and fiat currencies. By leveraging smart contracts on the blockchain, these digital instruments provide users with fractional ownership and the ability to engage in global markets without the need for conventional banking systems.
At the core of synthetic assets is their ability to mirror the price movements of underlying real-world assets. This is accomplished through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms where users can mint or trade these assets by locking collateral within smart contracts. The value of synthetic tokens is designed to reflect the behavior of their underlying counterparts, enabling users to benefit from market dynamics without holding the actual assets.
How Synthetic Assets Operate
The operation of synthetic assets hinges on several key components: collateralization, oracles, and smart contracts. To create synthetic assets, users must deposit collateral—typically in the form of cryptocurrency—into a smart contract. This collateral serves as a safeguard, ensuring that the synthetic asset maintains its value even during market fluctuations.
Oracles play a critical role by providing real-time price data from established financial markets, which is essential for maintaining the accuracy of synthetic asset values. Without reliable oracles, the integrity of synthetic asset pricing could be compromised, particularly during periods of high market volatility. Smart contracts automate the process of minting, updating prices, and managing collateral, ensuring a transparent and efficient trading environment.
Benefits of Synthetic Assets
Many investors are drawn to synthetic assets due to their flexibility and the unique opportunities they present. For instance, synthetic assets facilitate access to global markets, benefiting users in regions with limited access to traditional financial systems. They also allow for fractional ownership, enabling individuals to invest in expensive assets without requiring substantial capital.
Moreover, synthetic assets introduce innovative trading strategies, such as leveraged and inverse tokens, which can be advantageous for active traders looking to maximize gains or hedge against market downturns. The integration of these assets into the DeFi ecosystem further enhances their appeal, as users can stake, lend, or provide liquidity, generating passive income while remaining engaged with the underlying market.
Risks and Considerations
Despite their advantages, synthetic assets carry inherent risks that users must navigate carefully. Smart contract vulnerabilities pose potential threats, as any bugs or exploits could lead to significant financial losses. Additionally, issues with liquidity can arise, as some synthetic tokens may not have deep enough markets, resulting in slippage during trades.
Price volatility is another factor to consider; while synthetic assets track their underlying assets, they can behave unpredictably in rapidly changing markets. Users should also be aware of collateral requirements, as many protocols necessitate over-collateralization, tying up capital that could otherwise be utilized in other investments.
The Future of Synthetic Assets
Looking ahead, the landscape for synthetic assets in DeFi is poised for growth. As developers enhance price oracles and improve smart contract security, the appeal of synthetic assets will likely increase. Furthermore, as more yield-generating synthetic options become available, users will find new avenues to earn within the DeFi space.
In conclusion, while crypto synthetic assets offer a plethora of opportunities for accessing traditional markets and innovative investment strategies, users must approach these instruments with a solid understanding of the associated risks. As the technology and regulatory environment evolve, synthetic assets may well become a cornerstone of modern financial ecosystems.