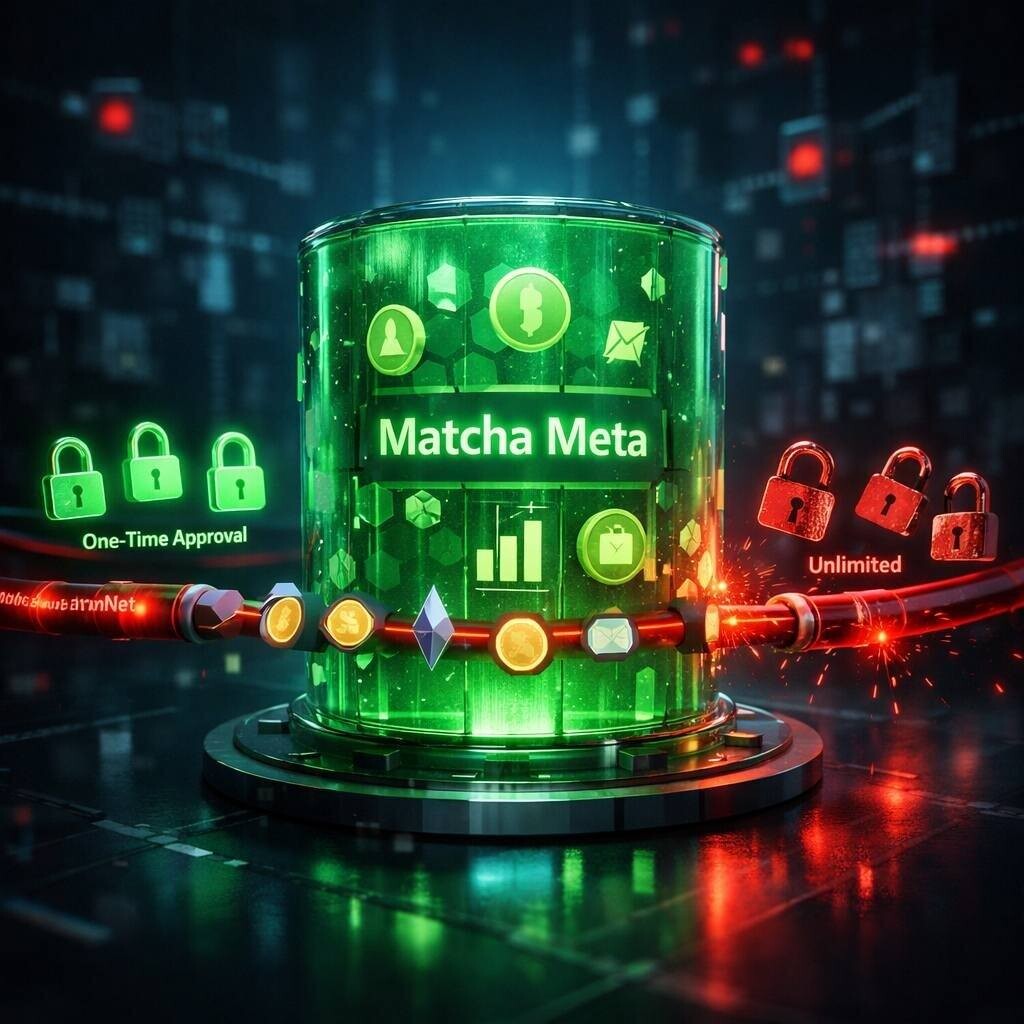
A significant security breach associated with the Matcha Meta platform has led to a staggering loss of nearly $17 million in cryptocurrency for its users. This incident, which unfolded on January 25 at approximately 5:10 PM London time, was deemed a breach by various reports detailing the event.
The Matcha Meta exchange, a decentralized finance (DeFi) aggregator developed by 0x, later acknowledged the breach and attributed the issue to a third-party integration. The integration in question was linked to SwapNet, an exchange aggregator that had been incorporated into the protocol.
Security firms, including Peckshield, were quick to flag the incident as it developed. In an update posted by Matcha Meta that evening, the team clarified that the breach was not related to 0x“s core components, specifically the AllowanceHolder or Settler contracts. Instead, they indicated that the losses stemmed from how certain user trades were routed through SwapNet.
As a meta aggregator, Matcha Meta serves as a unified interface for traders. It checks multiple decentralized exchange aggregators to determine the most efficient trading route while charging a minimal fee. This functionality, however, relies heavily on various integrations, each with its own security considerations. The platform”s statements suggest that the losses were primarily due to the integration with SwapNet, rather than flaws in its fundamental contracts.
In light of the hack, Matcha Meta issued warnings to users regarding potential exposure based on their approval settings and the routing of their trades. Users who had opted to disable One-Time Approvals and whose trades were routed through SwapNet faced heightened risks. The platform advised users to revoke any approvals granted to external aggregators beyond 0x“s One-Time Approval contracts.
In the realm of DeFi trading, users typically authorize a smart contract to spend the tokens being exchanged through an initial transaction. Some platforms provide an option for a one-time approval, while others allow for unlimited approvals that can remain active even after the transaction is completed. While persistent approvals can facilitate quicker trades and reduce transaction fees, they also pose a significant risk if the associated contract is breached. The Matcha Meta incident underscores the dangers linked to unlimited approvals and how they can lead to substantial losses.
This breach emerges amidst ongoing concerns within the DeFi sector regarding vulnerabilities in older smart contracts. A report by blockchain security firm Slowmist highlighted that hackers exploited weaknesses in code, resulting in over $649 million in thefts last year alone. The situation has reignited discussions about the implications of approval design choices and how they can lead to considerable financial repercussions.
In commentary shared on social media, DeFi security researcher Weilin Li noted that the incident appeared to involve an arbitrary call that enabled the attacker to drain the open allowance within the SwapNet contract. He characterized this breach as one of the most significant approval attacks observed, with the exception of phishing incidents.
Despite these insights, several crucial details remain ambiguous, particularly regarding how the attacker compromised the SwapNet smart contracts. As of now, SwapNet has not provided any comments, leaving many questions about the exact mechanism of the breach and what measures can be implemented to prevent similar occurrences in future integrations.
In summary, the Matcha Meta hack, attributed to SwapNet, has resulted in substantial losses for users, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in DeFi ecosystems. The platform has urged its users to take necessary precautions by revoking approvals granted to third-party aggregators, bringing renewed focus to the risks associated with unlimited approvals in decentralized finance.