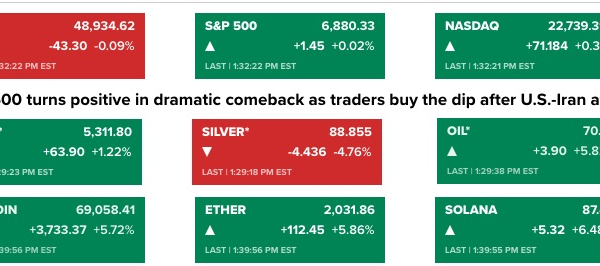
Renewed optimism is permeating global cryptocurrency markets as notable on-chain analyst Willy Woo has provided strong evidence indicating that Bitcoin reached a definitive price bottom in late December 2025. This development could pave the way for a substantial short-term rebound. Woo”s analysis is grounded in data-driven models that assess investment flows and miner behaviors, hinting at a recovery trajectory for the leading cryptocurrency despite ongoing macroeconomic challenges.
According to Woo”s recent findings, reported on January 15, 2026, December 24, 2025, is identified as the likely cyclical low point for Bitcoin. Investment inflows into Bitcoin exchange-traded funds and direct wallet purchases have shown consistent growth since that date, marking a reversal from prior outflows. Such patterns are generally regarded as reliable early indicators of shifting market sentiment.
Historically, Bitcoin has exhibited similar recovery patterns following past market cycles. For instance, the downturn from 2018 to 2019 was followed by a remarkable 300% price increase over the subsequent year. Likewise, the low observed in 2022 led to considerable gains throughout 2023 and 2024. Key metrics utilized in Woo”s models include:
- Network Value to Transactions (NVT) Ratio: This metric assesses the network”s valuation relative to its transaction volume.
- Miner Revenue Indicators: These indicators track the profitability and selling pressure stemming from mining operations.
- Exchange Net Flow: This monitors the movements of Bitcoin to and from trading platforms.
- Realized Price Distribution: This analyzes the cost basis of coins moving on the blockchain.
These indicators collectively suggest that the December 2025 low marks a “higher low” compared to previous cycle bottoms, indicating potentially stronger long-term fundamentals despite concerns over short-term volatility.
Woo”s insights into miner behavior during periods when Bitcoin trades below production costs are particularly noteworthy. Historically, such conditions do not typically trigger panic selling among miners. Instead, mining operations often adopt strategic responses that ultimately stabilize prices. When mining becomes unprofitable, miners frequently reduce output through various methods rather than liquidating reserves at a loss. These strategies include:
- Hash Rate Adjustment: Temporarily shutting down less efficient hardware reduces network difficulty, which lowers costs for remaining miners.
- Strategic Hedging: Utilizing futures and options to secure revenue mitigates immediate selling pressure on the spot markets.
- Operational Efficiency: Renegotiating energy contracts and optimizing operations lowers the overall production cost across the network.
This miner behavior establishes a “low-volume period” that effectively creates a temporary price floor. The recovery typically begins when Bitcoin”s price exceeds the average mining cost, prompting renewed production and investment. This pattern has been consistent across Bitcoin”s four major market cycles since 2011, providing historical context for the current situation.
The connection between Bitcoin”s market price and its production cost is among the most reliable indicators in cryptocurrency analysis. Data from the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance indicates that the global average Bitcoin mining cost fluctuated between $38,000 and $42,000 in late 2025. When Bitcoin”s price dipped below this range in December, mining operations representing around 15% of the network hash rate temporarily halted operations, creating a supply constraint. This, combined with steady institutional accumulation, contributed to establishing the December price bottom.
The gradual recovery above $42,000 in early January 2026 has already prompted some previously idled miners to resume operations, potentially initiating a positive feedback loop that supports further price appreciation.
Beyond technical metrics, Woo”s analysis also considers significant macroeconomic developments that could affect Bitcoin”s adoption trajectory. The recent executive order from President Donald Trump capping credit card interest rates at 10% could drive individuals toward decentralized financial solutions. While intended to protect consumers with lower credit scores, this regulation may inadvertently accelerate the adoption of cryptocurrency-based lending platforms and decentralized finance protocols that operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks.
Additional developments support this outlook:
- Increased Crypto Wallet Creation: December 2025 witnessed a 22% month-over-month rise in new non-custodial wallet addresses.
- Stablecoin Transaction Growth: Transactions involving dollar-pegged cryptocurrencies surged by 18% during the same period.
- DeFi Protocol Activity: Leading decentralized lending platforms reported a 31% increase in unique addresses.
These metrics indicate a growing engagement with cryptocurrency systems as alternatives to conventional financial products, particularly among demographics likely impacted by restrictions in the credit market.
Although short-term indicators suggest potential for Bitcoin price growth, Woo maintains a cautious perspective regarding the broader outlook for 2026. The ongoing decrease in global liquidity, particularly due to the reduction of central bank balance sheets in major economies, may pose challenges for all risk assets, including cryptocurrencies. The Federal Reserve”s continuous quantitative tightening measures, along with similar actions from the European Central Bank and the Bank of Japan, have resulted in a 12% contraction of the global monetary base since its peak in 2024.
Nonetheless, cryptocurrency markets have demonstrated an increasing decoupling from traditional risk assets in recent quarters. The correlation coefficient between Bitcoin and the NASDAQ index declined from 0.78 in early 2025 to 0.42 by December, indicating a growing independence from equity market fluctuations.
Institutional adoption may serve as a counterbalance to broader liquidity concerns. Major financial institutions have continued to expand their cryptocurrency services amidst the market downturn. For instance, BlackRock”s iShares Bitcoin Trust reached $25 billion in assets under management by January 2026, while Fidelity”s digital asset division increased its workforce by 40% during the last quarter of 2025.
This institutional infrastructure development lays a more robust foundation for sustained cryptocurrency adoption, irrespective of short-term fluctuations. Additionally, regulatory clarity has significantly improved in key markets. The European Union”s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework became fully operational in December 2025, providing comprehensive guidelines for cryptocurrency service providers across 27 member states. Similarly, Japan”s Financial Services Agency approved three additional cryptocurrency exchanges in November 2025, bringing the total to 48 licensed platforms in one of Asia”s prominent markets.
In conclusion, Willy Woo”s analysis presents a compelling case for the notion that Bitcoin established a significant price bottom in late December 2025, creating favorable conditions for short-term price appreciation. The combination of improving investment inflows, strategic miner behavior, and supportive macroeconomic developments suggests a potential for measured recovery in the near future. However, investors should remain aware of broader liquidity challenges that could impact the cryptocurrency landscape in 2026. This Bitcoin price prediction emphasizes the importance of integrating on-chain analytics with macroeconomic awareness when navigating the digital asset markets. As always, thorough research and risk management are crucial for participants in this evolving financial ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1: What specific date did Willy Woo identify as Bitcoin”s price bottom?
A1: Woo identified December 24, 2025, as the probable cyclical low point based on investment flow data and on-chain metrics showing reversal patterns beginning that date.
Q2: How does Bitcoin mining cost affect price support?
A2: When Bitcoin trades below production costs, miners typically reduce output rather than sell at a loss, creating supply constraints that establish temporary price floors until the market price recovers above mining costs.
Q3: What macroeconomic factor could drive Bitcoin adoption according to the analysis?
A3: President Trump”s credit card interest rate cap at 10% may inadvertently push individuals with lower credit scores toward alternative financial systems like Bitcoin and decentralized finance platforms.
Q4: What is the main caution for Bitcoin”s 2026 outlook?
A4: Decreasing global liquidity from central bank balance sheet reductions could create headwinds for all risk assets, though cryptocurrency markets show increasing decoupling from traditional financial markets.
Q5: How reliable is the mining cost price floor historically?
A5: This pattern has been observed in all four major Bitcoin market cycles since 2011, with prices consistently finding support near production costs before initiating recovery phases.
Disclaimer: The information provided is not trading advice. Bitcoinworld.co.in holds no liability for any investments made based on the information provided on this page. We strongly recommend independent research and/or consultation with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions.